Why Time Management Matters in Business
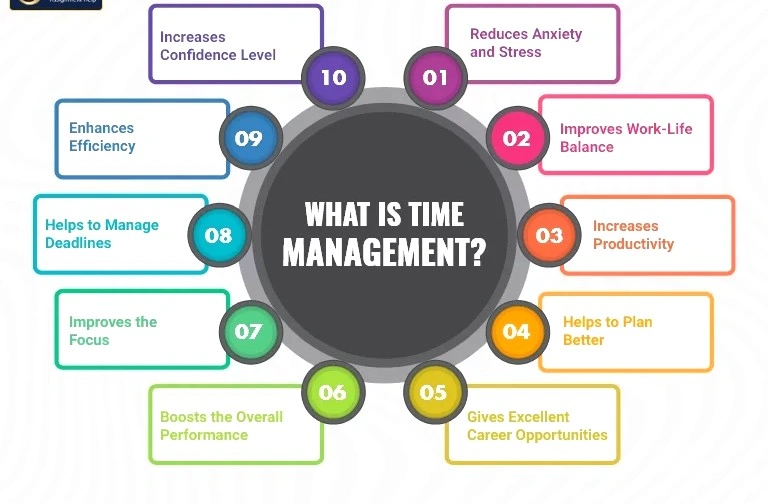
1. Increased Productivity
When tasks are planned and prioritized, more gets done in less time. Teams can focus on high-impact activities rather than reacting to crises.
2. Cost Efficiency
Delays are expensive. Efficient time use reduces overtime costs, avoids project overruns, and minimizes resource wastage.
3. Improved Decision Making
Good time management includes setting aside time for strategic thinking, which leads to more informed, forward-thinking decisions.
4. Employee Satisfaction
A well-structured schedule helps employees avoid burnout, meet deadlines comfortably, and maintain a better work-life balance.
5. Competitive Advantage
Time-efficient businesses are more agile, responsive, and capable of seizing market opportunities ahead of slower competitors.
Core Principles of Time Management in Business
1. Prioritization
Not all tasks are equal. Businesses must focus on what drives results—whether that’s serving key clients, delivering core services, or innovating for the future.
2. Planning
Daily, weekly, and quarterly planning ensures that all efforts are aligned with broader business goals. Good planning eliminates ambiguity and wasted effort.
3. Delegation
Managers must delegate tasks to the right team members to avoid bottlenecks and leverage the full capability of the workforce.
4. Goal Setting
Time must be allocated according to clear, measurable goals—whether they’re sales targets, product launches, or internal improvements.
5. Discipline
A time-managed organization needs a culture of discipline: meeting deadlines, starting meetings on time, and following schedules rigorously.
 Project Cloud Sneakers for Women
Project Cloud Sneakers for Women
 Retro Oval 90s Metal Sunglasses for Women
$17.99
Retro Oval 90s Metal Sunglasses for Women
$17.99
 The Holy Bible in Audio
$0.00
The Holy Bible in Audio
$0.00