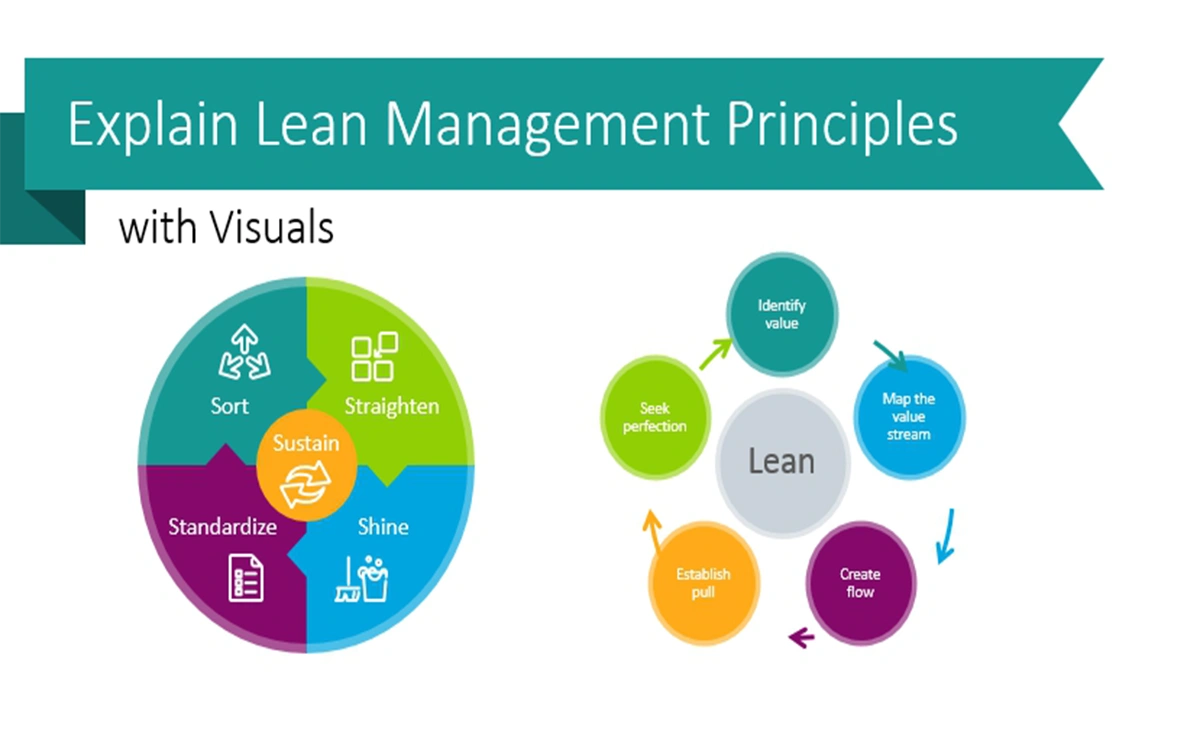
How Lean Management Works in Business Management
Now let’s walk through how Lean principles and tools come together to transform a business operation.
Step 1: Engage Leadership and Define Lean Vision
Lean transformations must start from the top. Executives and senior management need to:
- Articulate a clear Lean vision
- Align it with strategic goals
- Commit to cultural change
- Train leadership in Lean thinking
Without leadership buy-in, Lean initiatives often fail.
Step 2: Analyze Current State
Use Value Stream Mapping and process analysis to understand the current state of operations. Identify:
- Bottlenecks
- Delays
- Redundancies
- Quality issues
Example: In a customer service process, excessive email back-and-forth may be a source of waiting and motion waste.
Step 3: Identify and Eliminate Waste
Apply the 8 Wastes framework to determine where inefficiencies lie. Involve cross-functional teams to brainstorm improvements.
Example Actions:
- Reduce inventory levels to minimize storage costs
- Automate repetitive tasks to eliminate motion waste
- Combine steps in a process to reduce transport
Step 4: Redesign Processes for Flow and Pull
Reorganize workspaces, teams, and systems to create continuous flow—where value-adding steps are uninterrupted.
Implement pull systems using Kanban or other JIT techniques to ensure production or service delivery only occurs in response to real demand.
Step 5: Implement Standard Work and Visual Management
Once a new process is designed:
- Document it with Standard Work guidelines
- Use visual tools (like boards, dashboards, or signs) to make processes, progress, and issues visible to all
Step 6: Measure and Iterate
Lean is a continuous improvement loop:
- Measure KPIs (lead time, defect rates, throughput, customer satisfaction)
- Hold regular Kaizen events
- Empower employees to suggest and test improvements
This is where Lean shifts from a one-time project to a long-term organizational habit.
Benefits of Lean Management in Business
- Increased Efficiency
By eliminating waste, businesses achieve faster turnaround times and improved productivity. - Higher Quality
Lean emphasizes defect prevention and consistent processes, leading to fewer errors and rework. - Cost Reduction
Lean helps reduce operating costs through streamlined processes, better inventory control, and fewer resources used. - Greater Customer Satisfaction
By aligning operations with customer value, businesses deliver better experiences and solutions. - Employee Engagement
Lean empowers teams, encourages problem-solving, and fosters a culture of collaboration. - Scalability and Flexibility
Lean organizations can scale processes and respond to change more easily, adapting to new markets or customer needs.
Challenges of Lean Implementation
- Cultural Resistance
Employees accustomed to traditional systems may resist Lean practices, fearing job loss or increased scrutiny. - Misunderstanding Lean
Some leaders view Lean as cost-cutting rather than value-creating, leading to poor implementation. - Lack of Leadership Commitment
If management is not fully engaged, Lean becomes superficial and unsustainable. - Short-Term Focus
Lean requires long-term commitment. Companies expecting instant results often abandon it too soon.
Industries Using Lean Management
1. Manufacturing
Lean’s roots are in manufacturing, with companies like Toyota, GE, and Boeing using Lean to boost productivity and reduce waste.
2. Healthcare
Hospitals use Lean to reduce patient wait times, streamline admissions, and improve safety—examples include ThedaCare and Virginia Mason Medical Center.
3. Software Development
Lean principles underpin Agile and DevOps methodologies, enabling fast iterations and continuous delivery in companies like Spotify and Google.
4. Financial Services
Banks and insurers apply Lean to streamline back-office operations, reduce errors, and improve customer service.
5. Retail and E-commerce
Lean helps retailers like Amazon and Zara manage inventory more efficiently and respond quickly to demand changes.
Real-World Examples of Lean Management Success
Toyota
The pioneer of Lean, Toyota’s production system has become a global benchmark. Their focus on continuous improvement, employee empowerment, and waste elimination has made them one of the most efficient manufacturers in history.
Intel
Intel used Lean to reduce manufacturing cycle time by 60% and increase output without adding new resources, enabling faster delivery of chips to market.
Nike
Nike implemented Lean in its global supply chain, leading to a 50% reduction in lead time and significant environmental improvements.
Lean Management and Digital Transformation
As businesses digitize, Lean complements and accelerates transformation:
- Lean identifies inefficient processes before automation
- Digital tools enhance Lean visibility (e.g., IoT sensors, dashboards)
- Lean and Agile combine in software and service innovation
Lean + Digital = Smart, Responsive, and Efficient Enterprises
Lean Culture: Building a Lean Organization
Ultimately, Lean is not just about processes—it’s about people and mindset. A Lean organization:
- Encourages transparency and collaboration
- Supports experimentation and learning
- Rewards improvement efforts
- Respects every employee’s contributions
Companies like Toyota and Google demonstrate that culture is the foundation of sustainable Lean success.
Conclusion: Lean Management Is a Pathway to Sustainable Excellence
Lean Management offers a proven pathway to achieving operational excellence, improving customer satisfaction, and building adaptive, efficient, and resilient organizations.
By focusing on customer value, eliminating waste, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, Lean empowers businesses to:
- Do more with less
- React faster to change
- Build long-term competitive advantages
Whether you’re a startup founder, department manager, or corporate executive, applying Lean principles can help you unlock new levels of performance and innovation.
 Project Cloud Sneakers for Women
Project Cloud Sneakers for Women
 Retro Oval 90s Metal Sunglasses for Women
$17.99
Retro Oval 90s Metal Sunglasses for Women
$17.99
 The Holy Bible in Audio
$0.00
The Holy Bible in Audio
$0.00